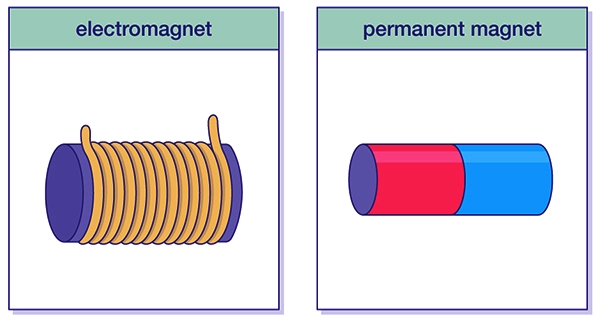
An electromagnet and a permanent magnet are both types of magnets, but they differ in how they are made and how they produce a magnetic field.
A permanent magnet is a material that generates a magnetic field without the need for an external power source. It is made from a material that is magnetized and retains its magnetism. Common materials used for permanent magnets include iron, cobalt, nickel, and certain alloys. A permanent magnet can hold its magnetic properties for a long time and can be used to produce a magnetic field that does not change over time.
An electromagnet, on the other hand, is a type of magnet that generates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. It is made by wrapping a wire around a magnetic core, such as iron or steel. When a current flows through the wire, it produces a magnetic field around the core. The strength of the magnetic field can be increased or decreased by changing the amount of current flowing through the wire.
One key advantage of an electromagnet is that its strength can be easily adjusted by changing the amount of current flowing through the wire. This makes it useful for a wide range of applications, from lifting heavy objects to controlling the movement of machines. In contrast, the strength of a permanent magnet is fixed and cannot be easily adjusted.
Another difference between electromagnets and permanent magnets is that electromagnets require a power source to produce a magnetic field, while permanent magnets do not. This means that an electromagnet can be turned on and off by controlling the flow of current through the wire, while a permanent magnet is always producing a magnetic field.
In summary, while both electromagnets and permanent magnets can produce a magnetic field, electromagnets require an external power source and their strength can be adjusted, while permanent magnets do not require an external power source, and their strength is fixed.