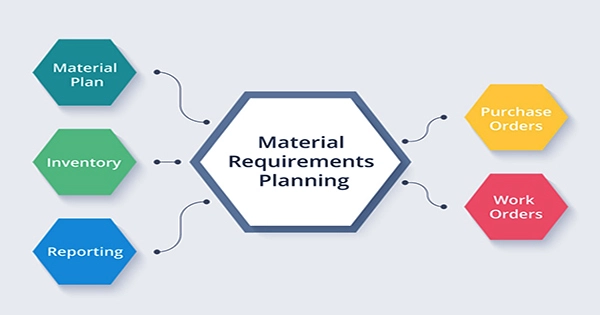
A technique for managing inventories that are digitally operated is material requirements planning. An MRP system can increase manufacturing process efficiency through just-in-time delivery and accurate material estimation.
Because they are in control of the manufacturing, purchasing, and delivery processes, manufacturers may maintain low production inventory levels with the use of material requirements planning. Production planning was previously all done manually using calculations for the reorder quantity and reorder point.
These computations assisted with purchase orders and helped to balance supply and demand, but the algorithms took a lot of time. Project management software today makes it easy to manage the planning of material requirements. You can match inventory to demand with the help of ProjectManager’s online Gantt charts.
Benefits of MRP: By using an MRP system, you can have your product’s raw materials and components on hand when you need them and reduce your inventory levels. This lowers the cost of stocking goods and guarantees that your business always has what it needs on hand.
Planning for material requirements also contributes to more effective inventory management and shorter customer lead times. Naturally, all of this results in a better production process for you. Each of these elements helps to boost revenue and satisfy customers. But that doesn’t mean that utilizing an MRP system is a bed of roses.
The main goal of MRP is to ensure that manufacturing happens as planned and that the necessary materials and components are available when they are required in the production process. Additional advantages of MRP include:
- shortened lead times for customers to boost customer satisfaction;
- less expensive inventory;
- effective inventory management and optimization — By purchasing or producing the ideal quantity and kind of inventory, businesses can reduce the danger of stock-outs and their detrimental effects on customer satisfaction, sales, and revenue, without spending more money on inventory;
- increased industrial efficiency by optimizing the usage of labor and equipment through effective production planning and scheduling;
- increased output at work;
- greater price competition for the goods.